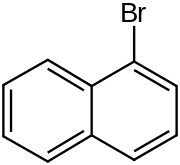
1-Bromonaphthalene
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Bromonaphthalene | |
| Other names
α-Bromonaphthalene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 90-11-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 6735 |
| EC Number | 201-965-2 |
| MeSH | C108222 |
| PubChem | 7001 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H7Br | |
| Molar mass | 207.07 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.48 g/mL |
| Melting point | 1-2 ºC |
| Boiling point | 132–135 °C at 12 mm; 145–148 °C at 20 mm |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1-Bromonaphthalene is an organic compound with the formula C10H7Br. It is one of two isomeric bromonaphthalenes, the other being 2-bromonaphthalene. This colorless liquid is used as a precursor to various substituted derivatives of naphthalene.
Synthesis and reactions
It is prepared by treatment of naphthalene with bromine:[1]
- C10H8 + Br2 → C10H7Br + HBr
The compound exhibits many reactions typical of aryl bromides. Bromide can be displaced by cyanide to give the nitrile. It forms a Grignard reagent[2] and organolithiuim compound. 1-Lithionaphthalene can be further lithiated to give 1,8-dilithionaphthalene, a precursor to peri-naphthalene compounds.
References
- ↑ H. T. Clarke and M. R. Brethen "α-Bromonaphthalene" Org. Synth. 1921, volume 1, 35. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.001.0035
- ↑ Henry Gilman, Nina B. St. John, and F. Schulze "α-Naphthoic Acid" Org. Synth. 1931, volume 11, 80. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.011.0080
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/4/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.