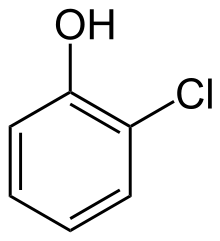
2-Chlorophenol
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Chlorophenol | |||
| Other names
o-Chlorophenol (no longer recommended[5]) 2-Hydroxychlorobenzene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| 95-57-8 | |||
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image | ||
| ChEBI | CHEBI:47083 | ||
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL108877 | ||
| ChemSpider | 13837686 | ||
| DrugBank | DB03110 | ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.213 | ||
| KEGG | C14219 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H5ClO | |||
| Molar mass | 128.56 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Light amber, liquid | ||
| Density | 1.2634 g/cm3 at 20 °C | ||
| Melting point | 9.4 °C (48.9 °F; 282.5 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 174.9 °C (346.8 °F; 448.0 K) | ||
| 20 g/L at 20 °C | |||
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether, benzene | ||
| Vapor pressure | 0.308 kPa | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 8.56 | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| 1.468 J·g−1·K−1 | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Main hazards | Corrosive - causes burns | ||
| Safety data sheet | MSDS | ||
| Flash point | 64 °C (147 °F; 337 K) | ||
| 550 °C (1,022 °F; 823 K) | |||
| Related compounds | |||
| Related aromatic hydrocarbons |
benzene phenol chlorobenzene | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| | |||
| Infobox references | |||
2-Chlorophenol or ortho-chlorophenol is an organic compound, a derivative of phenol. Related compounds are used as a disinfectant agents and various pesticides. This particular compound has few other applications, but is an intermediate in the polychlorination of phenol.[6] 2-chlorophenol is a colorless to amber liquid with an unpleasant, penetrating (carbolic) odor. It sinks in water and slowly dissolves.[7] The compound is known to be soluble in ethanol, ether, benzene, and caustic alkali solutions.[8]
See also
References
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 3–120, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, p. 1281, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 8–103, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, pp. 15–18, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ↑ Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 690. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
Only one name is retained, phenol, for C6H5-OH, both as a preferred name and for general nomenclature. The structure is substitutable at any position. Locants 2, 3, and 4 are recommended, not o, m, and p.
- ↑ Fiege, H.; Voges, H.-M.; Hamamoto, T; Umemura, S.; Iwata, T.; Miki, H.; Fujita, Y.; Buysch, H.-J.; Garbe, D.; Paulus, W. (2000), "Phenol Derivatives", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313
- ↑ http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/2-chlorophenol#section=Top
- ↑ Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 86TH Edition 2005-2006. CRC Press, Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, FL 2005, p. 3-110
External links
- ToxFAQs for Chlorophenols, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
- Compound Summary Compendium, PubChem Open Chemistry Database.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.