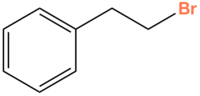
2-Phenylethylbromide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Bromoethylbenzene | |
| Other names
Phenethyl bromide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 103-63-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 7383 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.846 |
| PubChem | 7666 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H9Br | |
| Molar mass | 185.06 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless to yellow liquid |
| Density | 1.355g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −56 °C (−69 °F; 217 K) |
| Boiling point | 221 °C (430 °F; 494 K) |
| Insoluble in water | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 89 °C (192 °F; 362 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Phenylethylbromide is an organobromide that can be produced by the action of bromine and red phosphorus on 2-phenylethanol.
It is moderately toxic by ingestion.
When reacted with hydrazine, phenelzine is produced.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/17/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.