Alectinib
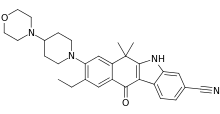 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Alecensa |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Multum Consumer Information |
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 1256580-46-7 |
| PubChem (CID) | 49806720 |
| DrugBank | DB11363 |
| ChemSpider | 26326738 |
| KEGG | D10542 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:90936 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H34N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 482.62 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Alectinib (marketed as Alecensa) is an oral drug that blocks the activity of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)[1][1][2] and is used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It was developed by Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Japan, which is part of the Hoffmann-La Roche group.
Approvals and indications
Approved in Japan in July 2014[3] for the treatment of ALK fusion-gene positive, unresectable, advanced or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer.[2]
Alecensa was approved by the US FDA in December 2015 to treat patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC whose disease worsened after, or who could not tolerate, treatment with crizotinib (Xalkori).[1]
Clinical trials
In a Japanese trial, after approximately 2 years, 19.6% of patients had achieved a complete response, and the 2-year progression-free survival rate is 76%.[2]
In Feb 2016 the J-ALEX phase III study comparing alectinib with crizotinib was terminated early because an interim anaysis showed that progression-free survival was longer with alectinib.[4]
References
- 1 2 3 New Oral Therapy To Treat ALK-Positive Lung Cancer. Dec 2015
- 1 2 3 McKeage, Kate (2014). "Alectinib: A Review of Its Use in Advanced ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer". Drugs. 75 (1): 75–82. doi:10.1007/s40265-014-0329-y. ISSN 0012-6667.
- ↑ Japan becomes first country to approve Roche’s alectinib for people with a specific form of advanced lung cancer
- ↑ Chugai’s ALK Inhibitor “Alecensa®” Trial Stopped Early for Benefit. Feb 2016
External links
- Alectinib UK Medicines Information