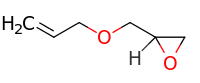
Allyl glycidyl ether
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(prop-2-enoxymethyl)oxirane | |
| Other names
AGE; 1-Allyloxy-2,3-epoxypropane; Glycidyl allyl ether; [(2-Propenyloxy)methyl] oxirane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| 106-92-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 13836520 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.131 |
| PubChem | 7838 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 114.2[1] |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | pleasant[1] |
| Density | 0.97 g/mL (20°C)[1] |
| Melting point | −100 °C; −148 °F; 173 K [1] |
| Boiling point | 154 °C; 309 °F; 427 K [1] |
| 14% (20°C)[1] | |
| Solubility in [[acetone, toluene, octane<ref name=Pubchem/>]] | miscible |
| Vapor pressure | 2 mmHg (20°C)[1] |
| Refractive index (nD) |
1.4348 (20°C)[2][3] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | poisonous, mild irritant[2] |
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| H226, H351, H341, H332, H302, H335, H315, H318, H317, H412 | |
| Flash point | 57 °C; 135 °F; 330 K [1] |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LC50 (median concentration) |
270 ppm (mouse, 4 hr) 670 ppm (rat, 8 hr)[4] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
10 ppm (45 mg/m3)[1] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 5 ppm (22 mg/m3) ST 10 ppm (44 mg/m3) [skin][1] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
50 ppm[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Allyl glycidyl ether is a glycidyl ether.
Preparation
Allyl alcohol and epichlorohydrin are the precursors to allyl glycidyl ether. They react in a condensation reaction and the product is subsequently treated with base to produce allyl glycidyl ether.[5]

Uses
Allyl glycidyl ether is used in adhesives and sealants.[2] It is also used in the production of polyvinylcaprolactam.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0019". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- 1 2 3 CID 7838 from PubChem
- ↑ Clayton, G. D. and F. E. Clayton (eds.). Patty's Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume 2A, 2B, 2C: Toxicology. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley Sons, 1981-1982., p. 2199
- ↑ "Allyl glycidyl ether". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Clayton, G. D. and F. E. Clayton (eds.). Patty's Industrial Hygiene and Toxicology: Volume 2A, 2B, 2C: Toxicology. 3rd ed. New York: John Wiley Sons, 1981-1982., p. 2197
- ↑ Kudyshkin, Mukhitdinova (1999). "Control of the molecular weight of polyvinylcaprolactam". Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry. 72 (10): 1846 – 1848.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/15/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.