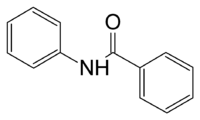
Benzanilide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-Phenylbenzamide | |
| Other names
N-Benzoylphenylamine | |
| Identifiers | |
| 93-98-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL115523 |
| ChemSpider | 6900 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.085 |
| PubChem | 7168 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H11NO | |
| Molar mass | 197.24 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.314 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 162 to 164 °C (324 to 327 °F; 435 to 437 K) |
| insoluble | |
| 2.71 | |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | External MSDS |
| Flash point | 141 °C (286 °F; 414 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Benzanilide or N-phenylbenzamide is a simple amide. Commercially available, it may be prepared by reacting benzoic acid and aniline directly.[1]
References
- ↑ Carl N. Webb (1941). "Benzanilide". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol., 1, p. 82
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/15/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.