Calone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
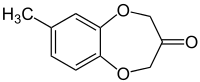
| IUPAC name
7-Methylbenzo[b][1,4]dioxepin-3-one | |
| Other names
Calone 1951; Watermelon ketone; Methylbenzodioxepinone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 28940-11-6 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 107218 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.044.823 |
| PubChem | 120101 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 178.19 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Calone or methylbenzodioxepinone, trade-named Calone 1951, also known in the industry as "watermelon ketone", was discovered by Pfizer in 1966. It is used to give the olfactory impression of a fresh seashore through the marine and ozone nuances. Calone is similar in structure of certain alicyclic C11-hydrocarbons like ectocarpene, excreted by some species of brown algae as pheromones.
Calone is an unusual odorant which has an intense "sea-breeze" note with slight floral overtones. It has been used as a scent component since the 1980s for its watery, fresh, ozone accords, and as a more dominant note in several perfumes of the marine trend, beginning in the 1990s.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.