Damnacanthal
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
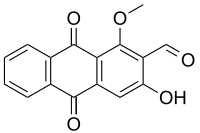
| IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-1-methoxy-9,10-dioxoanthracene-2-carbaldehyde | |
| Other names
3-Hydroxy-1-methoxyanthraquinone-2-aldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
| 477-84-9 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL212948 |
| ChemSpider | 2843 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.208.625 |
| PubChem | 2948 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H10O5 | |
| Molar mass | 282.25 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.461 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 532 °C (990 °F; 805 K) |
| Related compounds | |
| Related arylformaldehydes |
Gossypol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Damnacanthal is an anthraquinone which acts as a p56lck tyrosine kinase inhibitor.[1] It can be extracted from Morinda citrifolia.[2]
References
- ↑ Faltynek CR, Schroeder J, Mauvais P, et al. (September 1995). "Damnacanthal is a highly potent, selective inhibitor of p56lck tyrosine kinase activity". Biochemistry. 34 (38): 12404–10. doi:10.1021/bi00038a038. PMID 7547985.
- ↑ Anekpankul T, Goto M, Sasaki M, et al. (July 2007). "Extraction of anti-cancer damnacanthal from roots of Morinda citrifolia by subcritical water". Separation and Purification Technology. 55 (3): 343–349. doi:10.1016/j.seppur.2007.01.004.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/25/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.