Daphnia nivalis
| Daphnia nivalis | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Crustacea |
| Class: | Branchiopoda |
| Order: | Cladocera |
| Family: | Daphniidae |
| Genus: | Daphnia |
| Subgenus: | Ctenodaphnia |
| Species: | D. nivalis |
| Binomial name | |
| Daphnia nivalis Hebert, 1977 | |
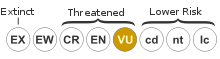
Daphnia nivalis is a species of water flea in the family Daphniidae, closely related to Daphnia carinata.[2] It is endemic to the Snowy Mountains of eastern Australia, where it lives only in water bodies that have existed for less than 20,000 years,[2] including Lake Cootapatamba, Australia's highest lake.[3] Due to its restricted range, it is listed as a vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List.[1]
References
- 1 2 J. Benzie (1996). "Daphnia nivalis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2.3 (2.3). International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 7 July 2011.
- 1 2 J. A. H. Benzie (1986). "Phylogenetic relationships within the genus Daphnia (Cladocera : Daphniidae) in Australia, determined by electrophoretically detectable protein variation". Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research. 37 (2): 251–260. doi:10.1071/MF9860251.
- ↑ J. A. H. Benzie (1984). "Zooplankton of an Australian high alpine lake, Lake Cootapatamba, Kosciusko Range". Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research. 35 (6): 691–702. doi:10.1071/MF9840691.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/6/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.