Degree matrix
In the mathematical field of graph theory the degree matrix is a diagonal matrix which contains information about the degree of each vertex—that is, the number of edges attached to each vertex.[1] It is used together with the adjacency matrix to construct the Laplacian matrix of a graph.[2]
Definition
Given a graph with the degree matrix for is a diagonal matrix defined as[1]
where the degree of a vertex counts the number of times an edge terminates at that vertex. In an undirected graph, this means that each new loop increases the degree of a vertex by two. In a directed graph, the term degree may refer either to indegree (the number of incoming edges at each vertex) or outdegree (the number of outgoing edges at each vertex).
Example
| Vertex labeled graph | Degree matrix |
|---|---|
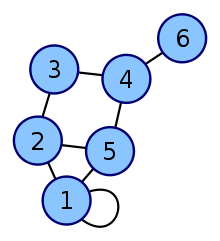 |
Properties
The degree matrix of a k-regular graph has a constant diagonal of .
References
- 1 2 Chung, Fan; Lu, Linyuan; Vu, Van (2003), "Spectra of random graphs with given expected degrees", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100 (11): 6313–6318, doi:10.1073/pnas.0937490100, MR 1982145.
- ↑ Mohar, Bojan (2004), "Graph Laplacians", in Beineke, Lowell W.; Wilson, Robin J., Topics in algebraic graph theory, Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications, 102, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 113–136, ISBN 0-521-80197-4, MR 2125091.