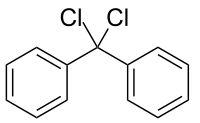
Diphenyldichloromethane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
diphenyldichloromethane | |
| Other names
bis-chlorodiphenylmethane; bisphenyldichloromethane; diphenyl-dichloromethane; dichlorodiphenylmethane; α,α-dichlorodiphenylmethane; 1,1-dichloro-1,1-diphenylmethane; 1,1-dichlorodiphenylmethane; benzophenone dichloride; | |
| Identifiers | |
| 2051-90-3 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| 1910601 | |
| ChemSpider | 15492 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.486 |
| PubChem | 16327 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H10Cl2 | |
| Molar mass | 237.12 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 1.235 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 146 to 150 °C (295 to 302 °F; 419 to 423 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 193 °C (379 °F; 466 K) at 32 torr[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Diphenyldichloromethane is an organic compound with the formula (C6H5)2CCl2. It is a colorless solid that is used as a precursor to other organic compounds.
Synthesis
It is prepared from carbon tetrachloride and anhydrous Aluminium chloride as catalyst in a double Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene.[3] Alternatively, benzophenone is treated with phosphorus pentachloride:[4]
- (C6H5)2CO + PCl5 → (C6H5)2CCl2 + POCl3
Reactions
It undergoes hydrolysis to benzophenone.[3]
- (C6H5)2CCl2 + H2O → (C6H5)2CO + 2 HCl
It is used in the synthesis of tetraphenylethylene,[5] diphenylmethane imine hydrochloride and benzoic anhydride.[6]
References
- ↑ Ballester, Manuel; Juan Riera-Figueras; Juan Castaner; Carlos Badfa; Jose M. Monso (1971). "Inert carbon free radicals. I. Perchlorodiphenylmethyl and perchlorotriphenylmethyl radical series". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 93 (9): 2215–2225. doi:10.1021/ja00738a021. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ↑ Andrews, L. J.; W. W. Kaeding (1951). "The Formation of Benzophenone and its Diethylketal in the Ethanolysis of Diphenyldichloromethane". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 73 (3): 1007–1011. doi:10.1021/ja01147a036. ISSN 0002-7863.
- 1 2 Marvel, C. S.; Sperry, W. M. (1941). "Benzophenone". Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol., 1, p. 95
- ↑ Spaggiari, Alberto; Daniele Vaccari; Paolo Davoli; Giovanni Torre; Fabio Prati (2007). "A Mild Synthesis of Vinyl Halides andgem-Dihalides Using Triphenyl Phosphite−Halogen-Based Reagents". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 72 (6): 2216–2219. doi:10.1021/jo061346g. ISSN 0022-3263. PMID 17295542.
- ↑ Inaba, S (1982). "Metallic nickel as a reagent for the coupling of aromatic and benzylic halides". Tetrahedron Letters. 23 (41): 4215–4216. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)88707-9. ISSN 0040-4039.
- ↑ "Preps in which diphenyldichloromethane appears". http://www.orgsyn.org. Retrieved 27 March 2013. External link in
|publisher=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/22/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.