Fensulfothion
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
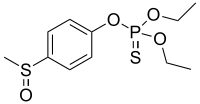
| IUPAC name
O,O-Diethyl O-[4-(methylsulfinyl)phenyl] phosphorothioate | |
| Identifiers | |
| 115-90-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 7991 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.741 |
| PubChem | 8292 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C11H17O4PS2 | |
| Molar mass | 308.35 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Brown liquid or yellow oil[1] |
| Density | 1.20 g/mL (20°C)[1] |
| 0.2% (25°C) | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | combustible[1] |
| US health exposure limits (NIOSH): | |
| PEL (Permissible) |
none[1] |
| REL (Recommended) |
TWA 0.1 mg/m3[1] |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) |
N.D.[1] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Fensulfothion is an insecticide and nematicide.[2] It is highly toxic and listed as an extremely hazardous substance.[3] It is widely used on corn, onions, rutabagas, pineapple, bananas, sugar cane, sugar beets, pea nuts, etc.[4]
External links
- Fensulfothion in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards #0284". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ↑ Fensulfothion, alanwood.net
- ↑ Appendix A List of Extremely Hazardous Chemicals
- ↑ Sunil Paul, MM; Aravind, UK; Pramod, G; Aravindakumar, CT (April 2013). "Oxidative degradation of fensulfothion by hydroxyl radical in aqueous medium.". Chemosphere. 91 (3): 295–301. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.11.033. PMID 23273737.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.