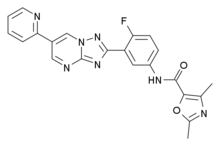
GNF6702
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| PubChem (CID) | 91810392 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:133824 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H16FN7O3 |
| Molar mass | 429.406 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
GNF6702 is the name for a broad-spectrum antiprotozoal drug invented by researchers working at the Genomics Institute of the Novartis Research Foundation in 2013,[1] with activity against leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness. These three diseases are caused by related kinetoplastid parasites, which share similar biology. GNF6702 acts as a non-competitive proteasome inhibitor which was effective against infection with any of the three protozoal diseases in mice, while having little evident toxicity to mammalian cells.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Biggart A, et al. Compounds and compositions for the treatment of parasitic diseases. US20150175613, priority date Dec 19, 2013
- ↑ Khare S, et al. Proteasome inhibition for treatment of leishmaniasis, Chagas disease and sleeping sickness. Nature 2016 doi:10.1038/nature19339
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.