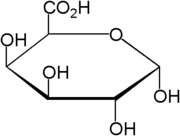
D-Galacturonic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4S,5R)-2,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxy-6-oxo-hexanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 6294-16-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:4153 |
| ChemSpider | 76444 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.621 |
| EC Number | 211-682-6 |
| PubChem | 84740 |
| UNII | CEP8I6411H |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O7 | |
| Molar mass | 194.139 |
| Melting point | 159 °C (318 °F; 432 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
D-Galacturonic acid is a sugar acid, an oxidized form of D-galactose. It is the main component of pectin, in which it exists as the polymer polygalacturonic acid.[1] In its open form, it has an aldehyde group at C1 and a carboxylic acid group at C6. Other oxidized forms of D-galactose are D-galactonic acid (carboxylic group at C1) and meso-galactaric acid (mucic acid) (carboxylic groups at C1 and C6). It is also a uronic acid or hexuronic acid. Naturally occurring uronic acids are D-glucuronic acid, D-galacturonic acid, L-iduronic acid and D-mannuronic acid.
References
- ↑ Debra Mohnen "Pectin structure and biosynthesis" Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2008, 11:266–277. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2008.03.006.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/4/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.