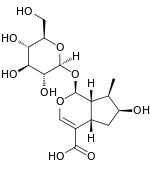
Loganic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(1S,4aS,6S,7R,7aS)-1-(β-D-Glucopyranosyloxy)-6-hydroxy-7-methyl-1,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-4-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 80905 |
| PubChem | 89640 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H24O10 | |
| Molar mass | 376.36 g·mol−1 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Loganic acid is an iridoid. Loganic acid is synthesized from 7-deoxyloganic acid by the enzyme 7-deoxyloganic acid hydroxylase (7-DLH).[1][2] It is a substrate for the enzyme loganate O-methyltransferase for the production of loganin.[3]
References
- ↑ Salim, Yu, Altarejos and De Luca (2013) Virus-induced gene silencing identifies Catharanthus roseus 7-deoxyloganic acid-7-hydroxylase, a step in iridoid and monoterpene indole alkaloid biosynthesis. The Plant Journal. 76(5). 754-765
- ↑ Miettinen, Dong, Navrot, Schneider, Burlat, et al. (2014) The seco-iridoid pathway from Catharanthus roseus. Nat Commun. 5(
- ↑ Dewick (2009) Medicinal Natural Products: A Biosynthetic Approach.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/3/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.