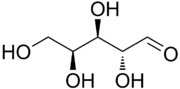
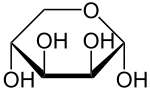
Lyxose
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R,3R,4S)-2,3,4,5-Tetrahydroxypentanal | |
| Other names
L-Lyxose Lyxopyranose | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1949-78-6 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1159661 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.149 |
| PubChem | 65550 |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10O5 | |
| Molar mass | 150.13 |
| Density | 1.545 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | 108 °C (226 °F; 381 K) |
| Soluble in water | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Lyxose is an aldopentose — a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including an aldehyde functional group. It has chemical formula C5H10O5. It is a C'-2 carbon epimer of the sugar Xylose.
Lyxose occurs only rarely in nature, for example, as a component of bacterial glycolipids.[1]
References
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/7/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.