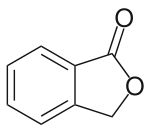
Phthalide
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Benzofuran-1(3H)-one | |
| Other names
Phthalolactone | |
| Identifiers | |
| 87-41-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:38085 |
| ChemSpider | 6621 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.586 |
| PubChem | 6885 |
| UNII | 8VV922U86J |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 134.13 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 75 to 77 °C (167 to 171 °F; 348 to 350 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 290 °C (554 °F; 563 K)[2] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Phthalide is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C8H6O2. It is a lactone that serves as the core chemical structure for a variety of more complex chemical compounds including dyes (such as phenolphthalein), fungicides (such as tetrachlorophthalide, often referred to simply as "phthalide") and natural oils (such as butylphthalide).
Examples
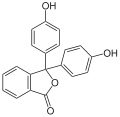 Phenolphthalein
Phenolphthalein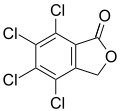 Tetrachlorophthalide
Tetrachlorophthalide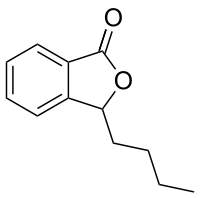 Butylphthalide
Butylphthalide
References
- ↑ Kumar, R. Arun; Maheswari, C. Uma; Ghantasala, Satheesh; Jyothi, C.; Reddy, K. Rajender (2011). "Synthesis of 3H-Quinazolin-4-ones and 4H-3,1-Benzoxazin-4-ones via Benzylic Oxidation and Oxidative Dehydrogenation using Potassium Iodide-tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide". Advanced Synthesis & Catalysis. 353 (2+3): 401–410. doi:10.1002/adsc.201000580.
- ↑ Kus, Nermin Simsek (2008). Asian Journal of Chemistry. 20 (2): 1226–1230. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/1/2015. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.