Pivaldehyde
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Pivaldehyde | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2,2-Dimethylpropanal | |
| Other names
Trimethylacetaldehyde Pivalaldehyde Neopentanal Neopentaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
| 630-19-3 | |
| ChemSpider | 11910 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.123 |
| Properties | |
| (CH3)3CCHO | |
| Molar mass | 86.13 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
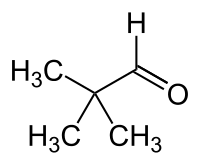
Pivaldehyde is an organic compound, more specifically an aldehyde. Shown in the image is a line-angle representation of this organic aldehyde, whose systematic name, 2,2-dimethylpropanal, is based on the longest carbon chain (three carbons), ending in "-al" to indicate the aldehyde functionality, and where another descriptive synonym is trimethylacetaldehyde.[1] Pivaldehyde is an example of an aldehyde with a sterically bulky R group, the tertiary-butyl group (with 3 methyl groups, at lower left in the image), attached to the carbonyl, >C=O. By definition, the other "group", R', is a hydrogen (H) atom, shown here pointing directly upward.
References
- ↑ Pubchem. "Trimethylacetaldehyde". nih.gov. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.