Rimeporide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 187870-78-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 9799487 |
| ChemSpider | 7975252 |
| UNII | QH6B4V5743 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2107802 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
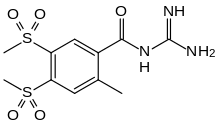
| Formula | C11H15N3O5S2 |
| Molar mass | 333.38 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Rimeporide is an experimental drug for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, being developed by the EspeRare foundation.[1] it has been granted orphan drug status by the European Medicines Agency.[2]
Mechanism of action
The substance blocks an ion pump called sodium–hydrogen antiporter 1 (NHE-1). While the exact mechanism is unknown, it is speculated that inhibition of this pump reduces sodium and calcium overload in cells of Duchenne patients.[1]
History
Rimeporide was designed as a treatment for chronic heart failure. It was unsuccessful in Phase I clinical trials, but was tolerated well by volunteers. Subsequently, the drug was sold to EspeRare, a Swiss nonprofit organisation[3] that aims at developing drugs for rare diseases. As of May 2015, the substance is in preclinical development for Duchenne.[1]
See also
Other drugs for Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Ataluren
- Biostrophin (experimental)
- Idebenone (experimental)
References
- 1 2 3 Spreitzer, Helmut (26 May 2015). "Neue Wirkstoffe – Rimeporid". Österreichische Apothekerzeitung (in German). 69 (11): 12.
- ↑ "EspeRare's Rimeporide receives Orphan Drug Designation in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy". EspeRare. 4 May 2015.
- ↑ "Our mission and vision". EspeRare. Retrieved 23 July 2015.