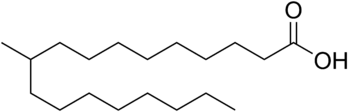
Tuberculostearic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
10-Methyloctadecanoic acid | |
| Other names
10-Methylstearic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 542-47-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 58549 |
| PubChem | 65037 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H38O2 | |
| Molar mass | 298.50 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Tuberculostearic acid is a saturated fatty acid produced by Actinomycetales bacteria.[1] The name 'Tuberculostearic acid' was coined because it was first isolated in 1927 from the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
References
- ↑ G.L. Frencha; C.Y. Chana; S.W. Cheunga; R. Teohb; M.J. Humphriesc; G. O'Mahony (18 July 1987). "Diagnosis of tuberculous meningitis by detection of tuberculostearic acid in cerebrospinal fluid". The Lancet. 330: 117–119. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92328-2.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 6/6/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.