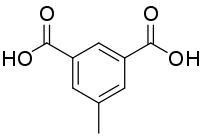
Uvitic acid
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
5-Methylisophthalic acid | |
| Other names
5-Methyl-1,3-benzenedicarboxylic acid; 3,5-Dicarboxytoluene | |
| Identifiers | |
| 499-49-0 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 61445 |
| EC Number | 207-881-2 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 180.16 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 298 °C |
| Boiling point | 408.7±33.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Vapor pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 215.1±21.9 °C |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Uvitic acid (5-methylisophthalic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(COOH)2.[1][2] The name comes from Latin uva which means a grape. The acid is called so because it may be produced indirectly from tartaric acid, which is found in the grape.[3] Under normal conditions, the acid is a white crystalline substance.
Preparation
Uvitic acid is obtained by oxidizing mesitylene or by condensing pyruvic acid with baryta water.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "Uvitic acid". rdchemicals.com. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ↑ "Uvitic acid". chemspider.com. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ↑ Senning, Alexander (2006). Elsevier's Dictionary of Chemoetymology: The Whys and Whences of Chemical Nomenclature and Terminology. Elsevier. p. 410. ISBN 9780080488813. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- ↑ "Definition of uvitic acid". merriam-webster.com. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/22/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.