Valkiri
| Valkiri | |
|---|---|
| Type | Multiple rocket launcher |
| Place of origin |
|
| Service history | |
| In service | 1982 – present[1] |
| Used by | South African National Defence Force |
| Wars |
South African Border War Angolan Civil War |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Denel, Somchem |
| Variants | Bateleur (40 launch tubes) |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 6,400 kg (14,080 lbs) |
| Length | 5.35 m (17 ft 7 in) |
| Width | 2.3 m (7 ft 7 in) |
| Height | 2.32 m (7 ft 7 in) |
| Crew | 2 |
|
| |
| Cartridge | HE-Fragmentation: 2.68 m (8 ft 10 in) |
| Caliber | 127 mm (5 in) |
| Barrels | 24 |
| Effective firing range | 36 km (22 mi) |
|
| |
| Engine | diesel |
| Suspension | Mercedes Benz Unimog 4×4 truck |
Operational range | 400 km (250 mi) |
| Speed | 90 km/h (56 mph) (road) |
The Valkiri is a South African self-propelled multiple rocket launcher. It is a 127mm system with a wheeled launcher vehicle, disposable pods, and fire control equipment developed by Denel Land Systems.[2] Contemporary models consist of a single launch module with five eight-cell rocket pods on a Unimog or SAMIL-100 carrier. Its mission is to engage in counter-battery strikes against hostile artillery and air defences as far as 22 km (13 mi) away. A full salvo of 40 127mm ripple fired projectiles with the HE submunition warhead will saturate a 1,500 m2 area with 388,000 anti-personnel bomblets in less than a minute.[3] Other potential warheads include cluster and an anti-tank mine dispenser.[4]
The system is based on the Soviet BM-21 Grad, which was deployed against South African expeditionary forces in Angola during Operation Savannah. Development was completed in 1981.[5] Valkiri's also played a key role in slowing the FAPLA advance in the 1987 Battle of Cuito Cuanavale.[6]
Variants
- Valkiri-22 Mk 1 (original version): 24 launch tubes mounted on a Unimog light 4x4 truck.
- Bateleur (current version): 40 launch tubes mounted on an armoured Samil 100 6x6 truck.
- Valkiri-5 a shortened lighter trailer-mounted version for airborne use. It has 12 launch tubes and uses a shortened version of the 127 mm rocket that has a maximum range of 5500 metres.[7]
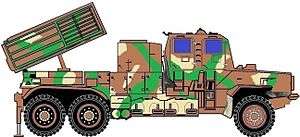 Bateleur 40 tube Multiple Rocket Launcher on SAMIL 100 armoured four door cab truck
Bateleur 40 tube Multiple Rocket Launcher on SAMIL 100 armoured four door cab truck
Operators
 South Africa - South African National Defence Force: 76 in reserve.[8]
South Africa - South African National Defence Force: 76 in reserve.[8]
References
- ↑ "Valkiri Multiple Launch Rocket System".
- ↑ "Valkiri Multiple Artillery Rocket". Retrieved 2006-10-25.
- ↑ Fact file: Denel FV2 Bateleur Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS)
- ↑ Bateleur
- ↑ Monick, S. The Forging of a Strike Force (Part I): Central themes in the history of the South African Army 1980-1990. Scientia Militaria, 1993, Volume 23 Issue 3 p. 364-377.
- ↑ "In Africa, Cheap and Deadly Rocket Launchers find a Niche". Retrieved 2016-01-11.
- ↑ Heitman, Helmoed-Römer (1990). South African Armed Forces. Cape Town, South Africa: Buffalo Publications. p. 123. ISBN 9780620148788.
- ↑ Leon Engelbrecht. "Denel FV2 Bateleur Multiple Launch Rocket System (MLRS)". Retrieved 5 November 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Multiple Launch Rocket System. |
- Army Recognition.com
- Photos at SA Bush War—halfway down the page