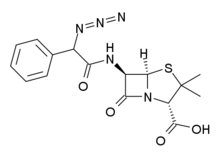
Azidocillin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral, IV, IM |
| ATC code | J01CE04 (WHO) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 57–64% |
| Biological half-life | 0.6-1.1 hrs |
| Excretion | 37–50% active substance in urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 17243-38-8 |
| PubChem (CID) | 71886 |
| DrugBank |
DB08795 |
| ChemSpider |
16735689 |
| UNII |
R8XDP7L3SL |
| KEGG |
D07235 |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:51758 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2105907 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H17N5O4S |
| Molar mass | 375.402 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Azidocillin is a type of penicillin.[1][2]
References
- ↑ Axelsson, A.; Jensen, C.; Melin, O.; Singer, F.; Von Sydow, C. (1981). "Treatment of acute maxillary sinusitis. V. Amoxicillin azidocillin, phenylpropanolamine and pivampicillin". Acta oto-laryngologica. 91 (3–4): 313–318. doi:10.3109/00016488109138513. PMID 6894819.
- ↑ Bergan, T.; Sørensen, G. (1980). "Pharmacokinetics of azidocillin in healthy adults". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 30 (12): 2185–2191. PMID 6894241.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.