Cytidine triphosphate
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
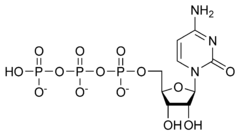
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methyl(hydroxy-phosphonooxyphosphoryl)hydrogen phosphate | |
| Other names
CTP; Cytidine-5'-triphosphate; Cytidine 5'-(tetrahydrogen triphosphate) | |
| Identifiers | |
| 65-47-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChemSpider | 19952488 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.556 |
| 1741 | |
| MeSH | Cytidine+triphosphate |
| PubChem | 6176 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H16N3O14P3 | |
| Molar mass | 483.156 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Cytidine triphosphate is a pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate.
CTP, much like ATP, consists of a ribose sugar, and three phosphate groups. The major difference between the two molecules is the base used, which in CTP is cytosine.
CTP is a substrate in the synthesis of RNA.
CTP is a high-energy molecule similar to ATP, but its role as an energy coupler is limited to a much smaller subset of metabolic reactions. CTP is a coenzyme in metabolic reactions like the synthesis of glycerophospholipids and glycosylation of proteins.
CTP acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme Aspartate carbamoyltransferase, which is used in pyrimidine biosynthesis.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Blackburn, G. Michael. Nucleic Acids in Chemistry and Biology. The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2006, p. 119-120.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.