Glisoxepide
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
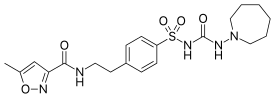
| IUPAC names
N-[2-[4-(azepan-1-ylcarbamoylsulfamoyl) phenyl]ethyl]-5-methyl-1,2-oxazole-3-carboxamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 25046-79-1 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL2106618 |
| ChemSpider | 30380 |
| DrugBank | DB01289 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.329 |
| KEGG | D07118 |
| PubChem | 32778 |
| UNII | H7SC0I332I |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H27N5O5S | |
| Molar mass | 449.52388 g/mol |
| Pharmacology | |
| A10BB11 (WHO) | |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Glisoxepide (INN) is an orally available anti-diabetic drug from the group of sulfonylureas.[1] It belongs to second-generation sulfonylureas.[2]
References
- ↑ Haupt E, Köberich W, Beyer J, Schöffling K (December 1971). "Pharmacodynamic aspects of tolbutamide, glibenclamide, glibornuride and glisoxepide. I. Dose response relations and repeated administration in diabetic subjects". Diabetologia. 7 (6): 449–54. doi:10.1007/bf01212061. PMID 5004178.
- ↑ Loubatières, A; Ribes, G; Mariani, MM; Alric, R. "Pharmacological Comparison Between Tolbutamide and Two Second Generation Hypoglycemic Sulfonylureas (Glibenclamide and Glisoxepide)". Acta diabetologica latina. 10 (2): 261–82. doi:10.1007/bf02590661. PMID 4200420.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.