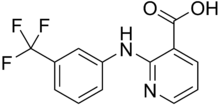
Niflumic acid
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | M01AX02 (WHO) M02AA17 (WHO) |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Biological half-life | 2.5 hr[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
4394-00-7 |
| PubChem (CID) | 4488 |
| IUPHAR/BPS | 2439 |
| ChemSpider |
4333 |
| UNII |
4U5MP5IUD8 |
| KEGG |
D08275 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL63323 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.289 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H9F3N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 282.21797 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| Melting point | 204 °C (399 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Niflumic acid is a drug used for joint and muscular pain. It is categorized as an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2. In experimental biology, it has been employed to inhibit chloride channels.[2] It has also been reported to act on GABA-A[3] and NMDA channels[4] and to block T-type calcium channels.[5]
References
- ↑ "Half life". Drug Bank. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- ↑ Knauf, Philip A.; Mann, Nancy A (1984). "Use of niflumic acid to determine the nature of the asymmetry of the human erythrocyte anion exchange system". J. Gen. Physiol. 83: 703–725. doi:10.1085/jgp.83.5.703. PMC 2215658
 . PMID 6736917.
. PMID 6736917. - ↑ Sinkkonen ST et al. (2003): Receptor subtype-dependent positive and negative modulation of GABA(A) receptor function by niflumic acid, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, Mol Pharmacol, p. 753-63. PMID 12920213
- ↑ Lerma J., Martin d.R. (1992). "Chloride transport blockers prevent N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-channel complex activation". Mol. Pharmacol. 41 (2): 217–222. PMID 1371581.
- ↑ Balderas E et al. (2012): Niflumic acid blocks native and recombinant T-type channels, J Cell Physiol, p. 2542-55. PMID 21898399
| Pyrazolones / Pyrazolidines | |
|---|---|
| Salicylates | |
| Acetic acid derivatives and related substances | |
| Oxicams | |
| Propionic acid derivatives (profens) |
|
| N-Arylanthranilic acids (fenamates) | |
| Coxibs | |
| Other | |
Items listed in bold indicate initially developed compounds of specific groups. #WHO-EM †Withdrawn drugs. ‡Veterinary use medications. | |
| Anti-inflammatory preparations, non-steroids |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capsaicin derivatives | |||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (blockers) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also: GABAergics • GHBergics • Glycinergics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also: Leukotrienergics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.