Laranjal do Jari
| Laranjal do Jari | |
|---|---|
| Municipality | |
| The Municipality of Laranjal do Jari | |
|
| |
| Nickname(s): "Beiradão" (Big Edge, because of the city's large boundary and its location in the edge of Amapá.) | |
| Motto: "Laranjal com Responsabilidade" (Laranjal with Responsibility) | |
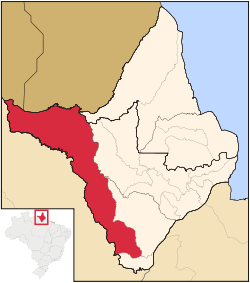 Location of Laranjal do Jari in the State of Amapá | |
| Coordinates: 00°51′20″S 52°32′21″W / 0.85556°S 52.53917°WCoordinates: 00°51′20″S 52°32′21″W / 0.85556°S 52.53917°W | |
| Country |
|
| Region | North |
| State |
|
| Founded | December 17, 1987 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Euricelia Melo Cardoso (PP) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 41,668 km2 (16,088 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 7 m (22 ft) |
| Population (2012) | |
| • Total | 39,285 |
| • Density | 0.94/km2 (2.4/sq mi) |
| [1] | |
| Time zone | UTC-3 (UTC-3) |
| HDI (2000) | 0.732 – medium[2] |
| Website | laranjaldojari.ap.gov.br |
Laranjal do Jari (Jari Orangery) is a municipality located in the west of the state of Amapá in Brazil. It is the only municipality in the west boundaries of Amapá, except for a small part of Vitória do Jari. Its population is 41,688 and its area is 29,699 km², which makes it the largest municipality of Amapá.
The municipality contains 39% of the 501,771 hectares (1,239,900 acres) Rio Cajari Extractive Reserve, created in 1990.[3] It also contains 69% of the 806,184 hectares (1,992,120 acres) Rio Iratapuru Sustainable Development Reserve, created in 1997.[4]
References
- ↑ "2012 Populational Estimate" (PDF). Censo Populacional 2012. Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). July 2012. Retrieved August 31, 2012.
- ↑ UNDP
- ↑ RESEX do Rio Cajari (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-11-06
- ↑ RDS do Rio Iratapuru (in Portuguese), ISA: Instituto Socioambiental, retrieved 2016-11-05
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/6/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.