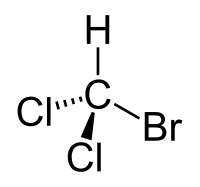
Bromodichloromethane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Bromo(dichloro)methane | |
| Other names
Bromodichloromethane Dichlorobromomethane | |
| Identifiers | |
| 75-27-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:34591 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL346231 |
| ChemSpider | 6119 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.779 |
| EC Number | 200-856-7 |
| KEGG | C14708 |
| PubChem | 6359 |
| RTECS number | PA5310000 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CHBrCl2 | |
| Molar mass | 163.8 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.980 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −57 °C (−71 °F; 216 K) |
| Boiling point | 90 °C (194 °F; 363 K) |
| 4.5 g/l at 20 °C | |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R45 R46 R20/21/22 R36/37/38 |
| S-phrases | S45 S26 S28 S27 S36/37/39 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Bromodichloromethane is a trihalomethane with formula CHBrCl2.
Bromodichloromethanehas been formerly used as a flame retardant, and a solvent for fats and waxes and because of its high density for mineral separation. Now it is only used as a reagent or intermediate in organic chemistry.
Bromodichloromethane can also occur in municipally-treated drinking water as a by-product of the chlorine disinfection process.[1]
Notes
- ↑ Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry, Accessed 07/10/2012, http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxfaqs/tf.asp?id=707&tid=127
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0393
- Bromodichloromethane at The Carcinogenic Potency Database
- Toxicological Profile at ATSDR
- Bromodichloromethane MSDS
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.