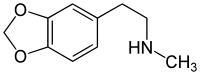
Homarylamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Various |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms |
1,3-benzodioxolyl-N-methyl-5-ethanamine; 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methyl-2-phenylethylamine |
| CAS Number | 451-77-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 10776 |
| ChemSpider | 10321 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2104353 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 179.21572 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Homarylamine (INN;[1] also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylphenethylamine or MDMPEA) is a substituted phenethylamine. It is the N-methylated analog of MDPEA.
Homoarylamine is known to have been patented for use as an antitussive agent.[2]
References
- ↑ "International Non-Proprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Preparations" (PDF). Chronicle of the World Health Organization. 12 (3). 1958.
- ↑ U.S. Patent 2,820,739
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.