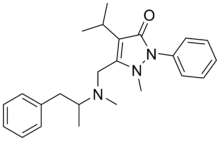
Famprofazone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | none |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 22881-35-2 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3326 |
| ChemSpider | 3209 |
| UNII |
HN0NCX453C |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1475693 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.153 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H31N3O |
| Molar mass | 377.52 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
Famprofazone (Gewodin, Gewolen) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent (NSAID) of the pyrazolone series which is available over-the-counter in some countries such as Taiwan.[1][2][3] It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic effects.[1][2] Famprofazone has been known to produce methamphetamine as an active metabolite, with 15-20% of an oral dose being converted to it.[4][5] As a result, famprofazone has occasionally been implicated in causing positives on drug tests for amphetamines.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 Swiss Pharmaceutical Society (2000). Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory (Book with CD-ROM). Boca Raton: Medpharm Scientific Publishers. p. 1932. ISBN 3-88763-075-0.
- 1 2 Hall, Judith A.; Morton, Ian (1999). Concise dictionary of pharmacological agents: properties and synonyms. Kluwer Academic. p. 342. ISBN 0-7514-0499-3.
- 1 2 Chan KH, Hsu MC, Tseng CY, Chu WL (2010). "Famprofazone use can be misinterpreted as methamphetamine abuse". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 34 (6): 347–53. doi:10.1093/jat/34.6.347. PMID 20663288.
- ↑ Oh ES, Hong SK, Kang GI (March 1992). "Plasma and urinary concentrations of methamphetamine after oral administration of famprofazone to man". Xenobiotica. 22 (3): 377–84. doi:10.3109/00498259209046649. PMID 1496827.
- ↑ Shin HS, Park BB, Choi SN, Oh JJ, Hong CP, Ryu H (1998). "Identification of new urinary metabolites of famprofazone in humans". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 22 (1): 55–60. doi:10.1093/jat/22.1.55. PMID 9491970.
| Pyrazolones / Pyrazolidines | |
|---|---|
| Salicylates | |
| Acetic acid derivatives and related substances | |
| Oxicams | |
| Propionic acid derivatives (profens) |
|
| N-Arylanthranilic acids (fenamates) | |
| Coxibs | |
| Other | |
Items listed in bold indicate initially developed compounds of specific groups. #WHO-EM †Withdrawn drugs. ‡Veterinary use medications. | |
| Opioids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paracetamol-type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NSAIDs |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cannabinoids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ion channel modulators |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Myorelaxants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.