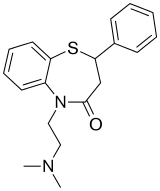
Tiazesim
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | None |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | SQ-10,496 |
| CAS Number |
5845-26-1 3122-01-8 (hydrochloride) |
| PubChem (CID) | 22107 |
| ChemSpider |
20775 |
| UNII |
44G76ZB85O |
| KEGG |
D02699 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL2111123 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H22N2OS |
| Molar mass | 326.456 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Tiazesim (INN; brand name Altinil), also known as thiazesim (BAN, USAN) or thiazenone, is a heterocyclic antidepressant related to the tricyclics which, first introduced in 1966 by Squibb Corporation (now Bristol-Myers Squibb), has since been discontinued and is no longer marketed.[1][2]
See also
References
- ↑ C. R Ganellin; D. J Triggle; F.. Macdonald (1997). Dictionary of pharmacological agents. CRC Press. p. 1973. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4. Retrieved 29 November 2011.
- ↑ The United States patents quarterly. 1969. Retrieved 1 May 2012.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.