Irampanel
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | None |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 206260-33-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 3038472 |
| ChemSpider | 2302037 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL29741 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
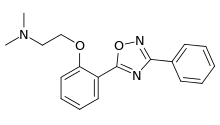
| Formula | C18H19N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 309.362 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Irampanel (INN, code name BIIR-561) is a drug which acts as a dual noncompetitive antagonist of the AMPA receptor and neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel blocker.[1][2] It was under development by Boehringer Ingelheim for the treatment of acute stroke/cerebral ischemia but never completed clinical trials for this indication.[3][4] Irampanel was also trialed, originally, for the treatment of epilepsy and pain, but these indications, too, were abandoned,[1] and the drug was ultimately never marketed.
References
- 1 2 Feigin V (June 2002). "Irampanel Boehringer Ingelheim". Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 3 (6): 908–10. PMID 12137411.
- ↑ Wang KK, Larner SF, Robinson G, Hayes RL (December 2006). "Neuroprotection targets after traumatic brain injury". Curr. Opin. Neurol. 19 (6): 514–9. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e3280102b10. PMID 17102687.
- ↑ Arunabha Ray; Kavita Gulati (1 January 2007). Current Trends in Pharmacology. I. K. International Pvt Ltd. pp. 321–. ISBN 978-81-88237-77-7.
- ↑ Weiser T (April 2005). "AMPA receptor antagonists for the treatment of stroke". Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 4 (2): 153–9. PMID 15857300.
| Calcium (Ca2+) |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium (K+) |
| ||||||
| Sodium (Na+) |
| ||||||
| Chloride (Cl−) |
| ||||||
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transporter (blockers) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also: GABAergics • GHBergics • Glycinergics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.