Cubitus valgus
| Cubitus valgus | |
|---|---|
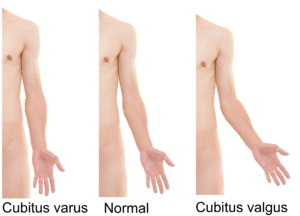 | |
| Cubitus varus versus cubitus valgus | |
| Classification and external resources | |
| Specialty | medical genetics |
| ICD-10 | M21.0, Q74.0 |
| ICD-9-CM | 736.01, 755.59 |
| DiseasesDB | 29423 |
Cubitus valgus is a medical deformity in which the forearm is angled away from the body to a greater degree than normal when fully extended. A small degree of cubitus valgus (known as the carrying angle) is acceptable and occurs in the general population.
When present at birth, it can be an indication of Turner syndrome[1] or Noonan syndrome. It can also be acquired through fracture or other trauma. The physiological cubitus valgus varies from 3° to 29°. Women usually have a more pronounced Cubitus valgus than men. The deformity can also occur as a complication of fracture of the lateral condyle of the humerus, which may lead to tardy/delayed ulnar nerve palsy.
The opposite condition is cubitus varus (736.02).
See also
References
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.