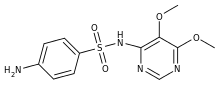
Sulfadoxine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATCvet code | QJ01EQ13 (WHO) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
2447-57-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 17134 |
| DrugBank |
DB01299 |
| ChemSpider |
16218 |
| UNII |
88463U4SM5 |
| KEGG |
D00580 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL1539 |
| NIAID ChemDB | 007816 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.732 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H14N4O4S |
| Molar mass | 310.33 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| | |
Sulfadoxine (also spelled sulphadoxine) is an ultra-long-lasting sulfonamide previously used in combination with pyrimethamine to treat or prevent malaria.[1] Due to high levels of resistance, its use is no longer recommended routinely.[2] It is also used, usually in combination with other drugs, to treat or prevent various infections in livestock.
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, a list of the most important medication needed in a basic health system.[3]
Mechanism of action
Sulfadoxine competitively inhibits dihydropteroate synthase, interfering with folate synthesis.
See also
References
- ↑ Medical Treatment - Sulphadoxine and Pyrimethamine.
- ↑ Matondo SI, Temba GS, Kavishe AA, et al. (2014). "High levels of sulphadoxine-pyrimethamine resistance Pfdhfr-Pfdhps quintuple mutations: a cross sectional survey of six regions in Tanzania.". Malar J. 13: 152. doi:10.1186/1475-2875-13-152. PMC 3998221
 . PMID 24751352.
. PMID 24751352. - ↑ "WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines" (PDF). World Health Organization. October 2013. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/11/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.