Hopantenic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
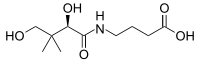
| IUPAC name
4-{[(2R)-2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl]amino}butanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 18679-90-8 17097-76-6 (Calcium salt) | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image Interactive image |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL2110783 |
| ChemSpider | 26309 |
| KEGG | D08042 |
| PubChem | 28281 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H19NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 233.26 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanoic acids |
|
| Related compounds |
Panthenol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Hopantenic acid (homopantothenic acid), also known as N-pantoyl-GABA, is a central nervous system depressant. Formulated as the calcium salt, it is used as a pharmaceutical drug in the Russian Federation for a variety of neurological, psychological and psychiatric conditions and sold as Pantogam (Russian: Пантогам).[1] It is not approved for use in Europe or the United States.
Chemistry
Hopantenic acid is a homologue of pantothenic acid. While pantothenic acid is the amide of D-pantoate and β-alanine, hopantenic acid is the amide of D-pantoate and γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). This change leads to an additional CH2 in the molecule.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ Pantogam, drugs.com
- ↑ Kopelevich VM, Evdokimova GS, Marieva TD, Shmuilovich LM (1971). "Synthesis of D-homopantothenic acid". Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 5 (9): 534–536. doi:10.1007/BF00771659.
External links
- pantogab (hopantenic acid) - Curehunter.com
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 8/27/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.