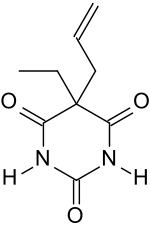
Ethallobarbital
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | N05CA20 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | Aethallymal, Aethylal, Etallobarbital, Go 1067 |
| CAS Number |
2373-84-4 |
| PubChem (CID) | 48542 |
| ChemSpider |
44152 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.412 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H12N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 196.203 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ethallobarbital (brand names Dormin, Dumex, Dormitiv, Dorval), also known as ethallymal and 5-allyl-5-ethylbarbituric acid, is an allyl-substituted barbiturate described as a sedative/hypnotic.[1][2][3][4][5] It was first synthesized in 1927.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 C.R. Ganellin; David J. Triggle (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. pp. 51–. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
- ↑ Martin Negwer (1978). Organic-chemical drugs and their synonyms: an international survey. Akademie-Verlag. ISBN 978-0-89573-100-5.
- ↑ Muller (19 June 1998). European Drug Index: European Drug Registrations, Fourth Edition. CRC Press. pp. 1440–. ISBN 978-3-7692-2114-5.
- ↑ Alberto Frigerio; Malcolm McCamish (1980). Recent Developments in Mass Spectrometry in Biochemistry and Medicine. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company.
- ↑ GOLDHAHN H, BARTH H (November 1953). "[Barbituric acids. II]". Pharmazie. 8 (11): 913–8. PMID 13133697.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/15/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.