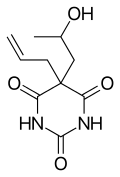
Proxibarbital
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | N05CA22 (WHO) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| Synonyms | Proxibarbital, Centralgol, Ipronal, 5-Allyl-5-(β-hydroxypropyl)barbituric acid |
| CAS Number |
2537-29-3 |
| PubChem (CID) | 17336 |
| ChemSpider |
16406 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.004 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14N2O4 |
| Molar mass | 226.229 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Proxibarbital (Ipronal) is a barbiturate derivative synthesized in 1956. It has anti-anxiety properties and in contrast to most barbiturates almost without hypnotic action.[1]
It was also used in the treatment of migraine headaches in a similar manner to butalbital.[2]
Valofane tautomerises to Proxibarbal in vivo.
References
- ↑ Zajdel, P.; Kulig, K.; Zejc, A. (2008). Zejc, A.; Gorczyca, M., eds. Chemia leków, podręcznik dla studentów farmacji i farmaceutów (in Polish). Warszawa, Poland. ISBN 978-83-200-3652-7.
- ↑ Sulman, F. G.; Pfeifer, Y.; Tal, E. (1976). "Migraine therapy by enzyme induction with proxibarbital". Therapie der Gegenwart (in German). 115 (12): 2088–2103. PMID 14412.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 7/9/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.