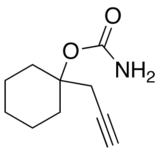
Hexapropymate
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | N05CM10 (WHO) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
358-52-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 9661 |
| ChemSpider |
9280 |
| UNII |
0J9RN2PRJ7 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL2104292 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.018 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H15NO2 |
| Molar mass | 181.232 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Hexapropymate is a hypnotic/sedative. It has effects similar to those of barbiturates and was used in the 1970s-1980s in the treatment of insomnia before being replaced with newer drugs with improved safety profiles.[1]
References
- ↑ Gustafsson, L. L.; Berg, A.; Magnusson, A.; Malmlund, H. O.; Sandell, B. M.; Stig, R. (1989). "Hexapropymate self-poisoning causes severe and long-lasting clinical symptoms". Medical toxicology and adverse drug experience. 4 (4): 295–301. doi:10.1007/bf03259914. PMID 2770531.
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/26/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.