Butobarbital
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Soneryl |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | N05CA03 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
77-28-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 6473 |
| DrugBank |
DB01353 |
| ChemSpider |
6229 |
| UNII |
OHZ8QAW6YC |
| KEGG |
D02618 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL404422 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.928 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
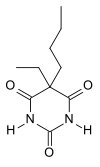
| Formula | C10H16N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 212.246 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Butobarbital (BAN), also called butobarbitone or butethal, Soneryl, and Neonal,[1] is a hypnotic drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It was developed by Poulenc Brothers (now part of Rhône Poulenc) in 1921.[2]
References
- ↑ International Drug Names
- ↑ DE Patent 481129
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.