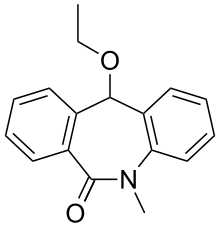
Etazepine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | None |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | 88124-27-0 |
| PubChem (CID) | 65662 |
| ChemSpider | 59097 |
| UNII | SBC76K7XWC |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL2106559 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.081.231 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 267.322 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
Etazepine (INN) is an anticonvulsant with a tricyclic structure which is related to the benzodiazepines, but was never marketed.[1] It appears to exert its effects via acting through the GABAergic system.[1]
See also
References
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
| Classes |
|
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (TCAs and TeCAs) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Others |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 5/30/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.