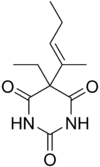
Vinbarbital
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | N05CA09 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
2430-49-1 |
| PubChem (CID) | 5284636 |
| ChemSpider |
4447681 |
| UNII |
7NZH2C1T6O |
| KEGG |
D07321 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL503565 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.309 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H16N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 224.256 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Vinbarbital is a hypnotic drug which is a barbiturate derivative.[1] It was developed by Sharp and Dohme in 1939.[2]
References
- ↑ Mueller, V. A. (1950). "An analysis and evaluation of vinbarbital sodium for obstetric amnesia and analgesia". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 59 (3): 679–684. doi:10.1016/0002-9378(50)90253-5. PMID 15405833.
- ↑ US 2187703
| Alcohols | |
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids | |
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines |
|
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: GABAergics | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.